Stunning Maillard Reaction Chemical Formula

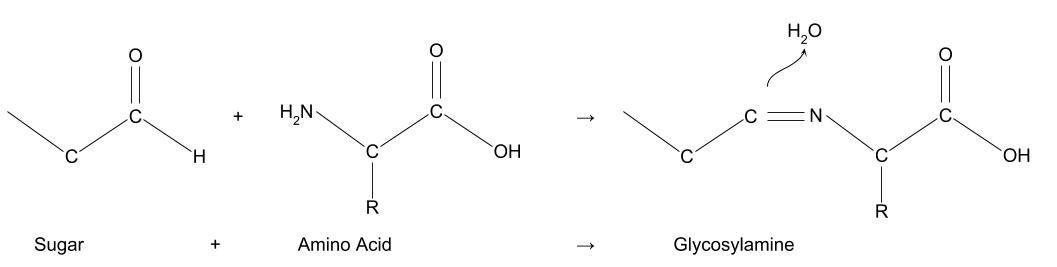
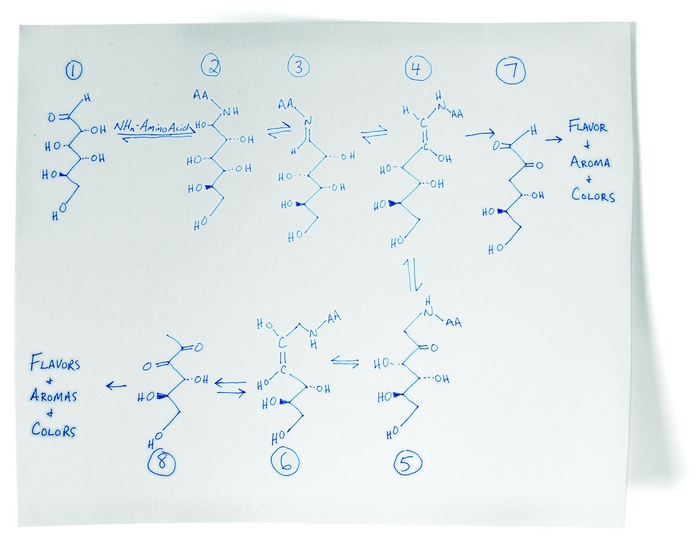
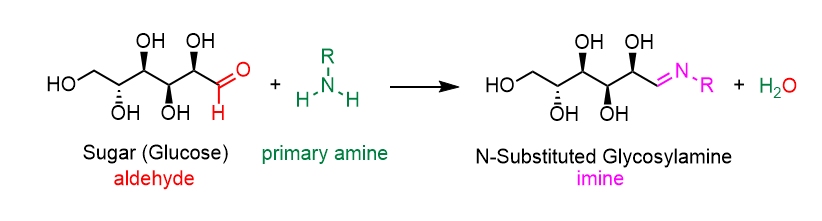
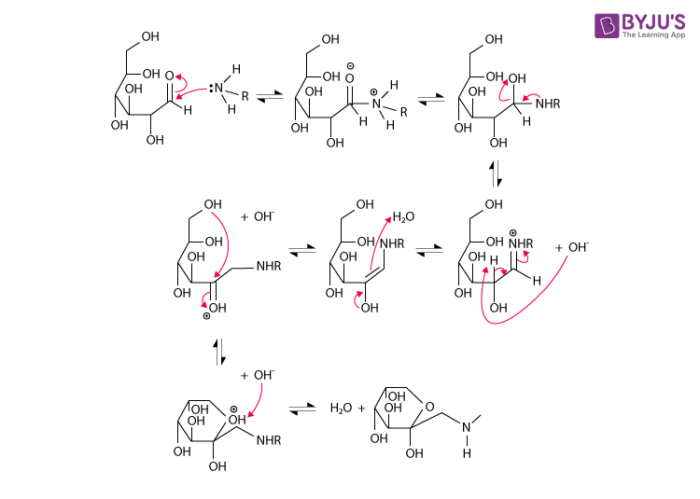
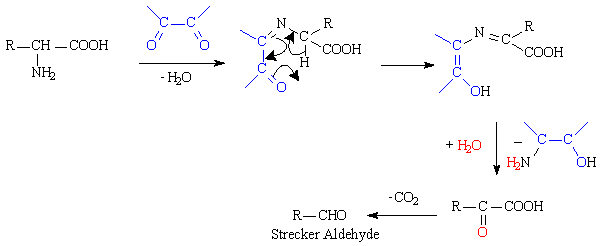
The Maillard reaction is the result of chemical reactions between a carbonyl group of the reducing sugar present and a free amino group of the protein or amino acid which forms a lactosyl-lysine also known as Schiffs base 25.
Maillard reaction chemical formula. Monosodium glutamate MSG also known as sodium glutamate is the sodium salt of glutamic acidMSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese. In the vast majority of infant formulas lactose is the main reducing sugar present while proteins are found as casein and whey proteins. The next step in caramelization starts off with the glucose and fructose which are in solution in water.
What is Maillard reaction. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty savory flavor of food as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups. This reaction is a kind of non-enzymatic browning.
The reaction is also used in sunless tanning formulas. C12H22O11 sucrose H2O water heat C6H12O6 glucose C6H12O6 fructose This reaction simplified into a chemical reaction above is called sucrose inversion. The Maillard Reaction.
The Maillard reaction is the name given to the set of chemical reactions between amino acids and reducing sugars that causes browning of foods such as meats breads cookies and beer. This reaction is responsible for the characteristic flavour and aroma of browned food. The Maillard reaction is the reaction between a nitrogen-containing molecule particularly the amino acids lysine and proline in the case of meats and grains respectively and a reducing sugar.
An amino-group is made of one nitrogen atom and two hydrogen atoms. Sugars in their linear noncyclic form and amino acids. Such as caramel or roasting.
The Maillard reaction is named after the French chemist Louis Camille Maillard. A spontaneous reaction even at temperatures as low as 25 C. The Maillard Reaction is named after the French scientist Louis Camille Maillard 1878 - 1936 He studied the reaction of amino acids and carbohydrates in 1912 as part of his PhD thesis.