Peerless Anaerobic Chemical Equation
The Chemical Oxygen Demand COD is used to quantify the amount of organic matter in waste streams and predict the potential for biogas pro-duction.
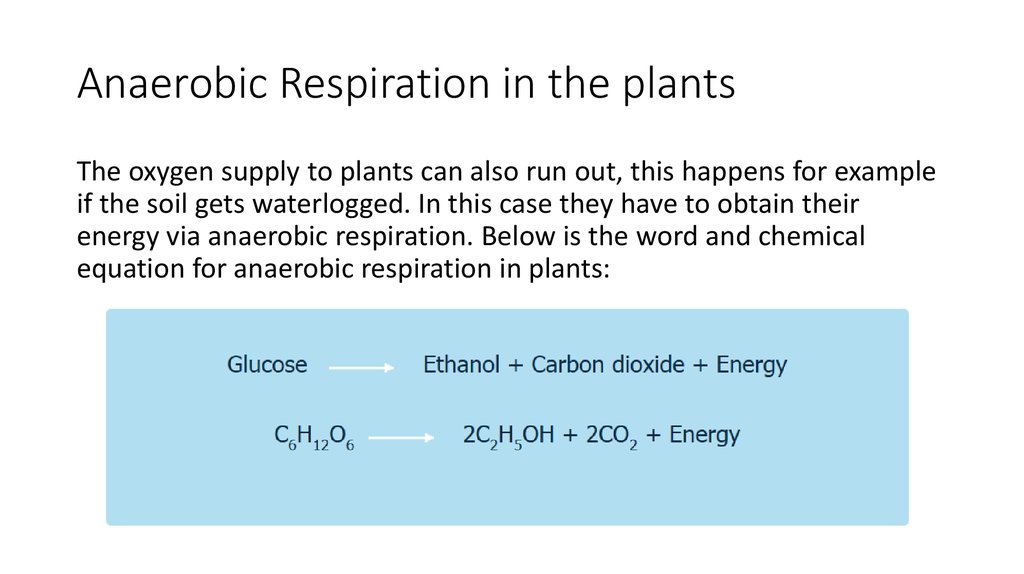
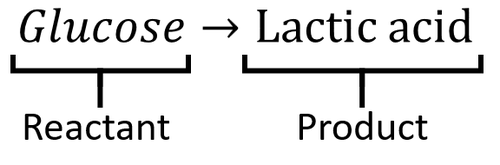
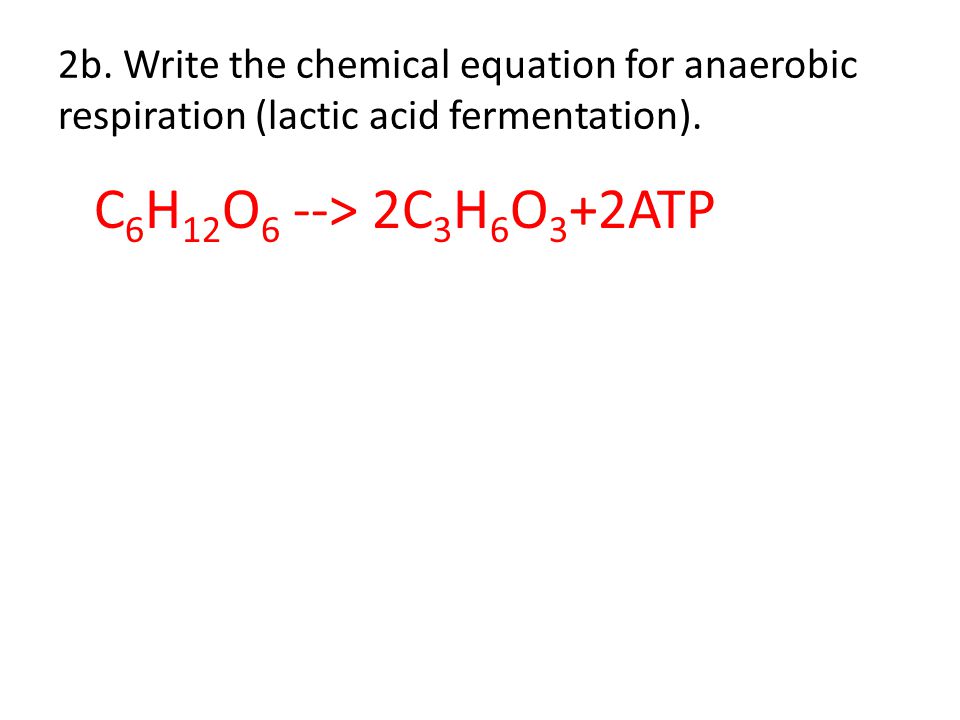
Anaerobic chemical equation. Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation lactic acid fermentation and in decomposition of organic matter. The chemical equation is C6H12O6 - 2C3H6O3 Glucose - Lactic acid. The chemical version of this aerobic respiration equation is.
Anaerobic digestion AD is a biological process that breaks down organic materials feedstocks in the absence of oxygen anaerobic conditions into methane CH 4 and carbon dioxide CO 2It is a process that occurs naturally in bogs lake sediments oceans and digestive tracts. What is Anaerobic Respiration. C6H12O6 2 NAD 2 ADP 2 P ----- 2 pyruvic acid CH3COCOOH 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 H.
Stoichiometry of Anaerobic Digestion CnHaObNc H2O xCH4 yCO2 zHCO3- zNH4 x y and z are a function of n a b and c methane production biogas production digester pH potential inhibition Organic Feedstock Theoretical General Equation Buswell 1952 digester alkalinity. This video is p. Its chemical equation is as follows.
The product of glycolysis is pyruvate that used in anaerobic respiration fermentation. This occurs in microorganisms but is. You need to be able to recognise the chemical symbols.
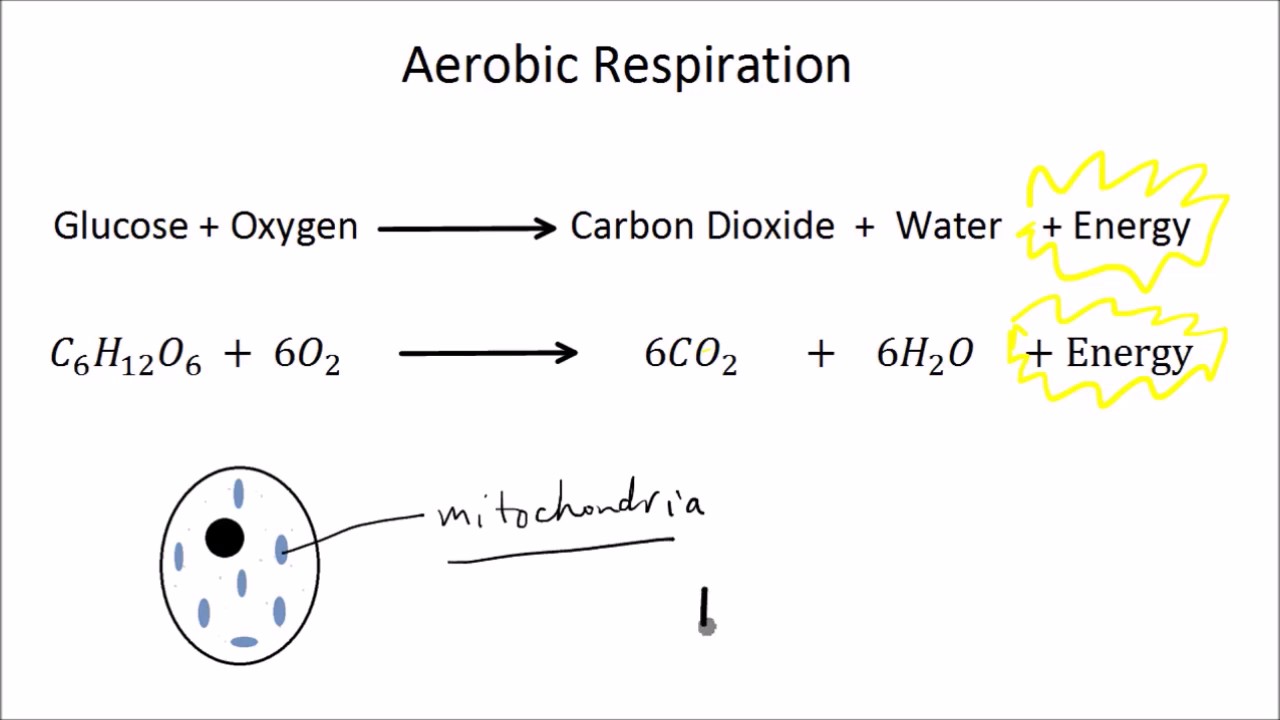
Glucose is oxidised to release its energy. Glycolysis is a series of biochemical reactions that break down a glucose molecule into two molecules of pyruvic acid. Though it does not produce as much energy as aerobic respiration it gets the job done.
Glucose C6H12O6 Oxygen 6O2. Learn about the two types of respiration. Glucose enzymes carbon dioxide ethanol lactic acid.